With the increasing digitalization of business, companies are facing an exponential increase in data, both internally generated and customer-generated. Data is stored in different databases and exists in multiple forms. To take full advantage of these sources of information and generate value, it is necessary to be able to combine and analyze the various sources of data in the company, and even to compare them in real-time with data available as Open Data. To do this, several methods exist, including Data Virtualization. This method is extremely efficient because it reduces storage costs and integration times while guaranteeing unified, real-time access to data sources without replicating or moving them. How can you do this? Read our article below.
Data Lake, Enterprise Data Warehouse, or Data Virtualization?
With the increasing digitalization of business activities, companies are increasingly faced with an exponential increase in data, generated internally or by their customers. The data is stored in different databases and has many forms: structured data from transactional systems or unstructured data such as emails, images, videos, PDFs, data from IoT, geolocation data, maintenance data, manufacturing process data, system logs, etc.
To take full advantage of these sources of information and generate value, it is necessary to be able to combine and analyze the various sources of data in the company and even to compare them in real-time with data available as Open Data.
To achieve this objective, companies are faced with organizational and technical challenges. Data security and governance have become essential to provide the company’s businesses with a data catalog and self-service access. To meet these challenges, data architects often recommend gathering and copying all data sources into a single system to ensure data security and governance, such as an Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) or a Data Lake.
The data stored in an EDW is transformed and structured to make it directly searchable by BI tools, while in Data Lakes the data is raw and unstructured. Unlike Data Warehouses, Data Lakes are more used by Data Engineers and Data Scientists to work on large raw data sets. The storage costs in a Data Warehouse are however much higher than in a Data Lake like Hadoop or AWS S3 designed for low-cost storage. Data lakes and data warehouses are optimized for different purposes and should be used for what they were designed for. However, these two approaches to mass storage can be unified through Data Virtualization.
Duplication or virtualization?
Connecting data sources (CRM, ERP, IoT, cloud) to the EDW or the Data Lake requires the implementation and maintenance of workflows for their loading. This activity generates duplication of data, delays, and costs each time new sources are added. This can severely damage the organization’s agility when it comes to proposing and integrating new data-driven services. By using direct connectors to sources, data virtualization reduces storage costs, integration time, and its costs. It makes it easy and cost-effective to federate and connect disparate and dispersed sources of data across the enterprise, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
What is Data Virtualization?
Data Virtualization is an agile data integration technology that provides unified, real-time access to data sources without replicating or moving them. It allows you to create a vision that federates the data available through business views using very different and dispersed sources. To guarantee performance, cache and join optimization mechanisms are implemented.
The Data Virtualization layer provides generic access via standard protocols (JDBC, ODBC, REST, SOAP…). Therefore, the complexity of data access and query optimization is hidden. The user only interacts with the Data Virtualization engine via SQL language while the sources can use other more complex query dialects. Data Virtualization also provides a layer of fine-tuned management of security and access to these views. It also provides a “Data Catalog” to enable the business to quickly find the Datasets they need in a self-service manner.
Data Virtualization Use Case for an Agile Business Data Platform
If you only have a few data sources to federate, you probably don’t need a data virtualization solution. Instead, Data Virtualization will be relevant to unify multiple data sources such as CRM, ERP, application databases, Data Lake, and/or Data Warehouse on-premise or in the cloud.
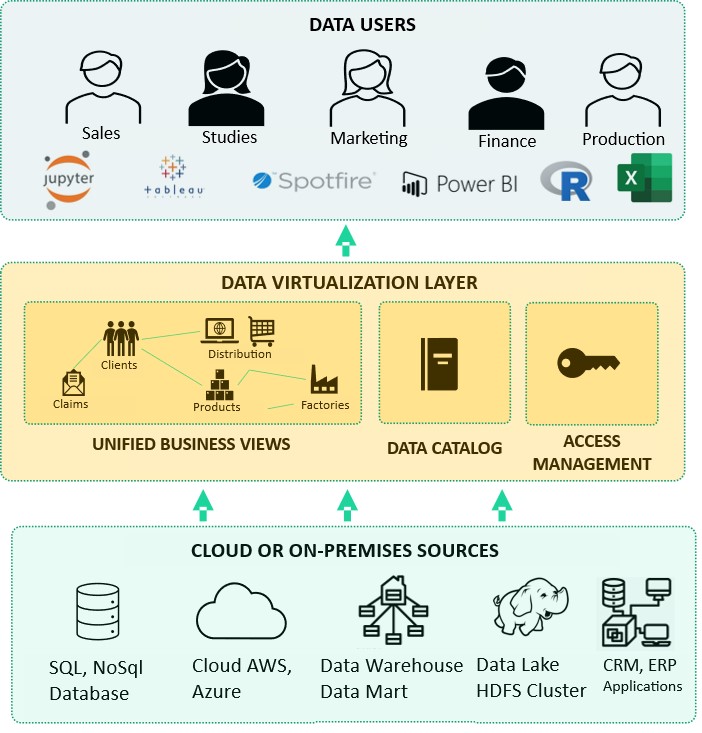
How long does it take to implement a business data platform using Data Virtualization?
In a few weeks, it is possible to federate a set of disparate databases by providing a “Data Catalog” with self-service datasets in different formats (JDBC, ODBC, REST, SOAP). Business views are directly accessible to traditional BI tools or data scientists. Implementation can be fast. Indeed, Data Virtualization uses the storage and computing infrastructures already in place. There are no more data transfer workflows to set up, which can be long and complex. All you have to do is to set up the connectors to access the data sources. During the implementation of the solution, the data engineer can focus on the semantics of the data and the definition of the business views rather than on the synchronization and replication of data without added value for the company.
Sources:
